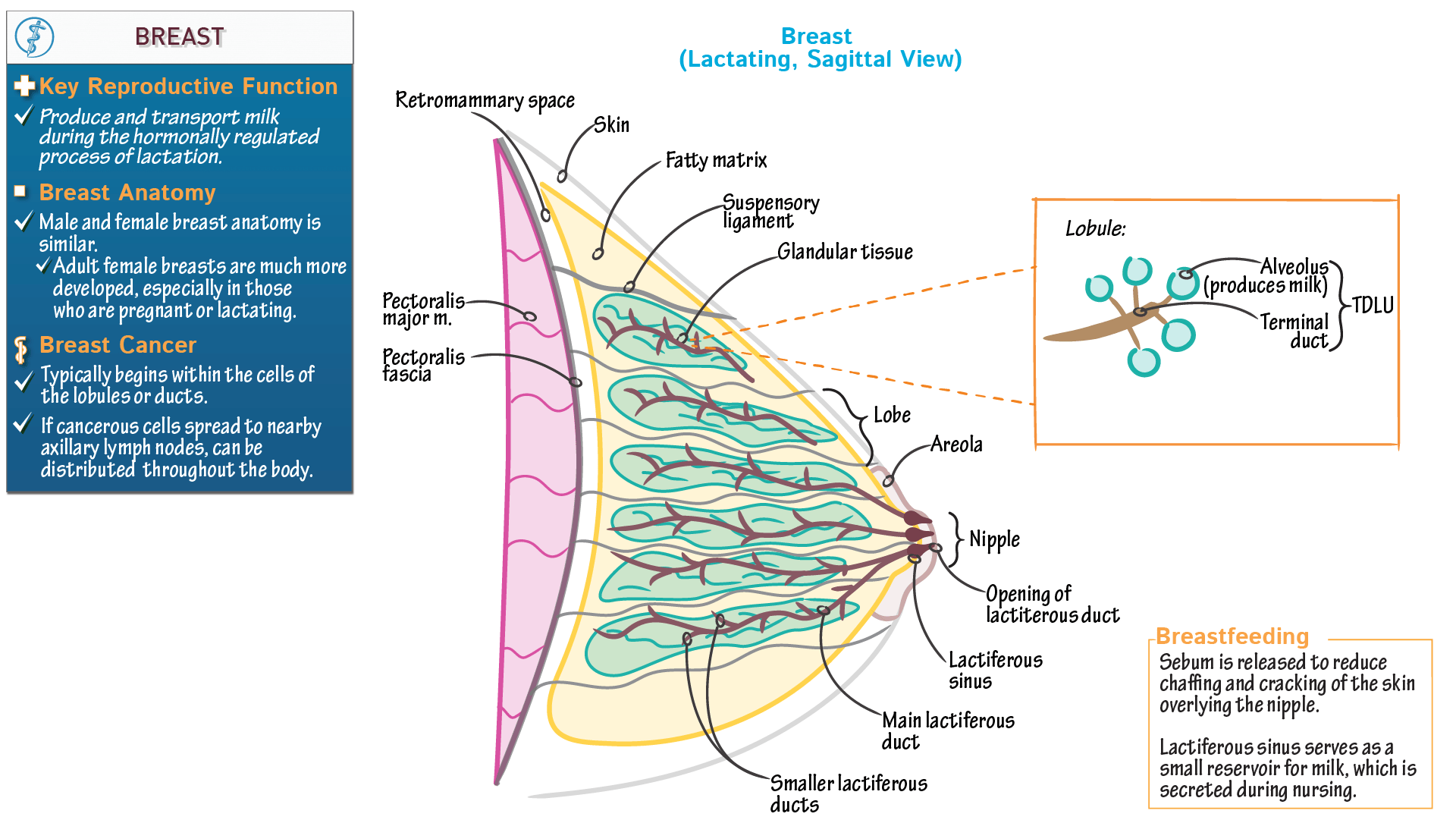
Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryological tissues Female external genital organs the 'vulva' or the female external genital organs, are those genital organs that are present on the surface of the female body and can be easily examined without the use of any special instruments The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males
Reproductive System: Breast | ditki medical & biological sciences
There is also considerable variation in size between individuals
Permanent breast growth during puberty.
But the sexualization of boobs in popular culture — from celebrating ‘sexy’ cleavage to shaming women who breastfeed in public to banning women’s nipples on social media — has led them to be a privately celebrated and consequently publicly taboo organ in society. Breasts can serve both biological and sexual functions, making them complex organs in human anatomy The biological function of breasts breasts primarily serve a biological purpose tied to reproduction and nurturing In females, they produce milk through a process called lactation, which is crucial for feeding infants
This function is a key aspect of mammalian biology, as it ensures the. Breasts are not an organ per se but a distinctive region of skin and subcutaneous tissue Some examples of sex organs include the vulva (which includes the vagina) and penis, while reproductive organs include the uterus and testicles Breasts are not an organ per se but a distinctive region of skin and subcutaneous tissue.
These movements challenge the narrow definitions of sexual propriety and push for a more nuanced, humanized understanding of the breast as both a sexual and social organ
Breasts in parenthood and bonding beyond romance one of the most ancient and powerful roles of the breast is in nourishing life. Breasts are both part of the reproductive anatomy (anatomy The female breasts are considered the accessory organs of reproduction

