Both sexes develop breasts from the same embryological tissues The main parts of the female anatomy can be classified as external and internal parts The relative size and development of the breasts is a major secondary sex distinction between females and males
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE ANATOMY& PHYSIOLOGY - ppt video online download
There is also considerable variation in size between individuals
Permanent breast growth during puberty.
The dual nature of breasts—as both nurturing organs and objects of sexual attraction—creates a complex dynamic that varies across different cultures and individual preferences Cultural perspectives on breasts cultural attitudes toward breasts vary widely around the world. A key concern in feminist rhetoric has always been the unwarranted sexualization of breasts Breasts might be secondary sex organs, but they aren’t inherently sexual in nature
Breasts serve a purpose in reproduction, i.e Producing milk and feeding a newborn But the sexualization of boobs in popular culture — from celebrating ‘sexy’ cleavage to shaming women who. Breasts are considered accessory organs of the female reproductive system, located far from other reproductive organs
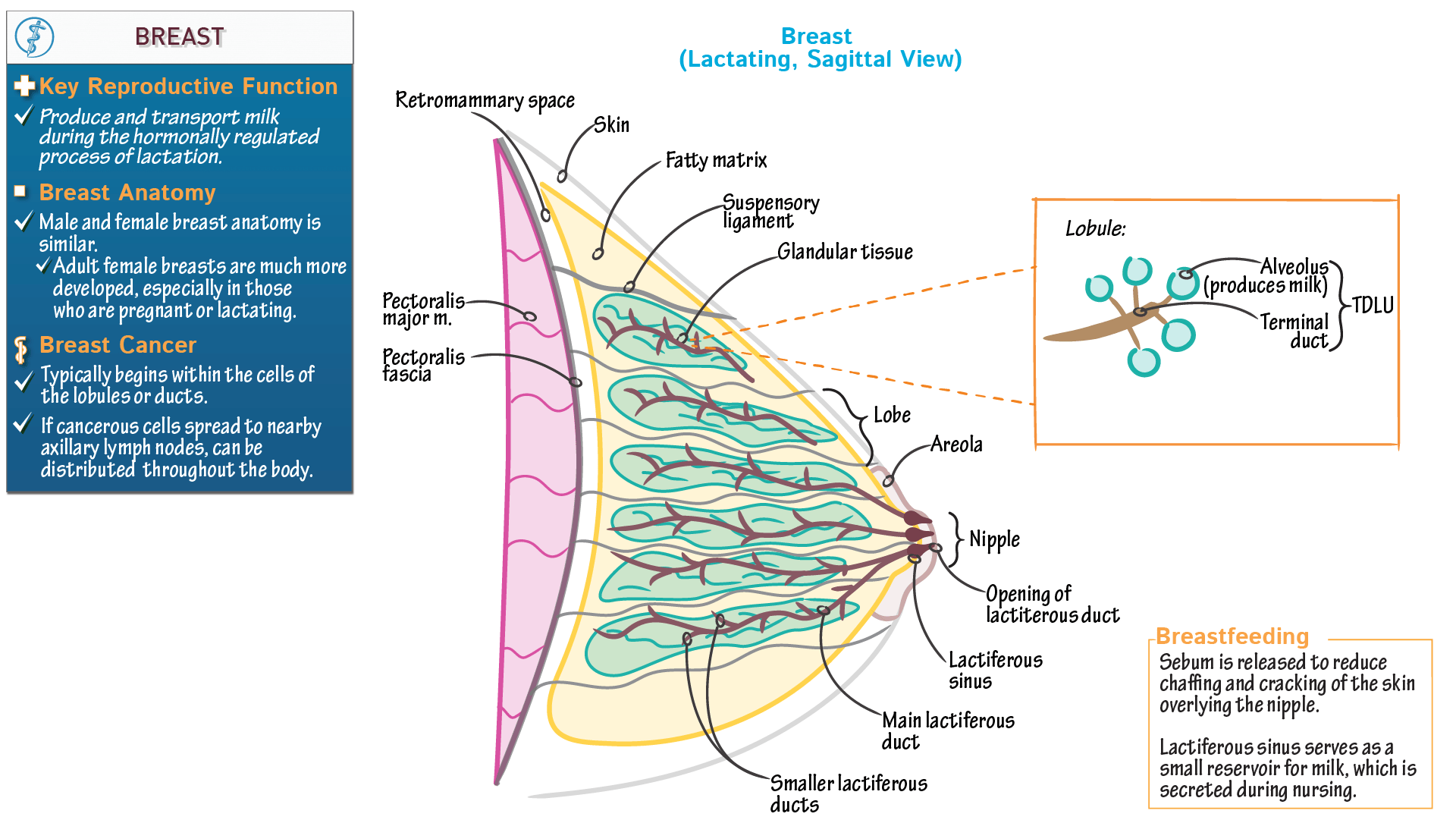
They are responsible for supplying milk to an infant during lactation, a process that occurs after childbirth.
Breasts are primarily associated with lactation and sexual attraction They consist of glandular tissue and fat, and their size and shape can vary greatly among individuals On the other hand, vaginas are the reproductive organs responsible for sexual intercourse, childbirth, and menstruation. The female reproductive system is essential for hormone regulation, sexual pleasure, pregnancy, breastfeeding, and more

