The sample is taken from an artery, not a vein, and healthcare providers typically order it in certain emergency situations. It also measures your blood's ph levels An arterial blood gases (abg) test is a blood test that measures the acidity, or ph, and the levels of oxygen (o2) and carbon dioxide (co2) from an artery
Arterial Blood Gas Interpretation - Clinical Case Study
The test is used to check the function of the patient’s lungs and how well they are able to move oxygen into the blood and remove carbon dioxide.
Ensure proper sampling of blood specimen
Consider repeating abg if results do not fit the patient history and clinical scenario A venous blood gas (vbg) can also be checked to see if it correlates with abg results (only pao2 should be different). Interpreting an arterial blood gas (abg) is a crucial skill for physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, and other health care personnel Abg interpretation is especially important in critically ill patients
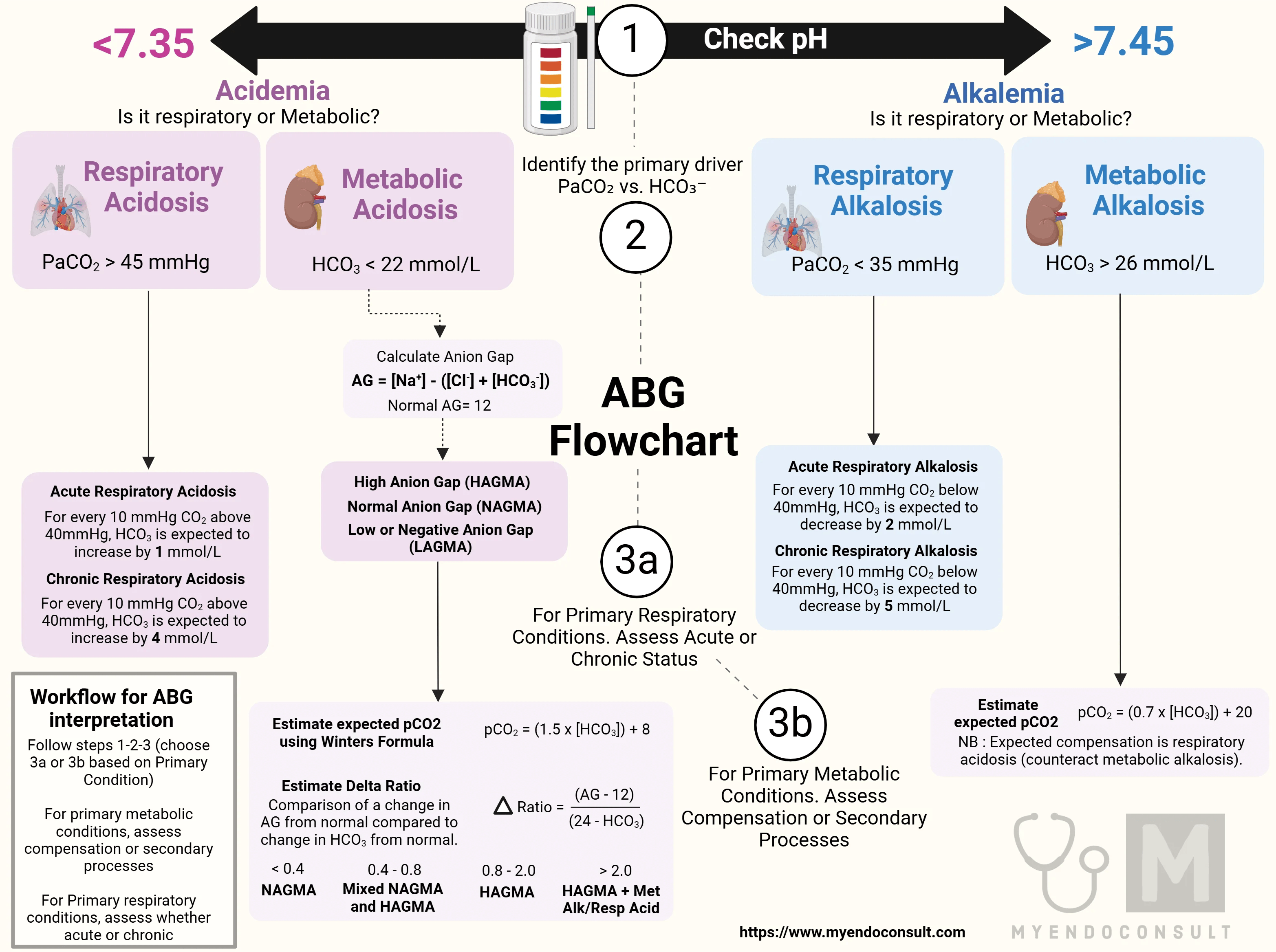
Arterial blood gas (abg) interpretation is something that can be difficult to grasp initially (we’ve been there) We’ve created this guide, which aims to provide a structured approach to abg interpretation whilst also increasing your understanding of each result’s relevance. An arterial blood gas (abg) test measures oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in your blood An abg test measures the blood gas tension values of the arterial partial pressure of oxygen (pao2), and the arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (paco2), and the blood's ph.

An arterial blood gas (abg) test measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, and acidity in your blood to see how well your lungs, heart and kidneys are working.
An arterial blood gas (abg) test is a diagnostic procedure that measures the amounts of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the arterial blood This test is crucial for evaluating a person’s lung function and how well oxygen and carbon dioxide are being transported and removed from the body. Summary the abg test helps your healthcare provider evaluate your lung and kidney function The test measures the balance between oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood