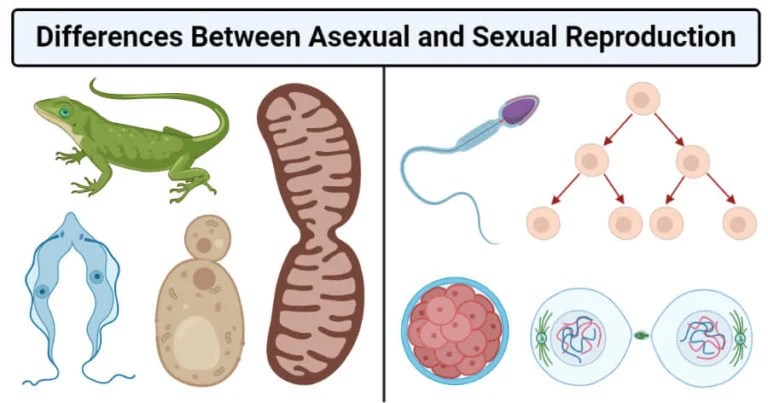
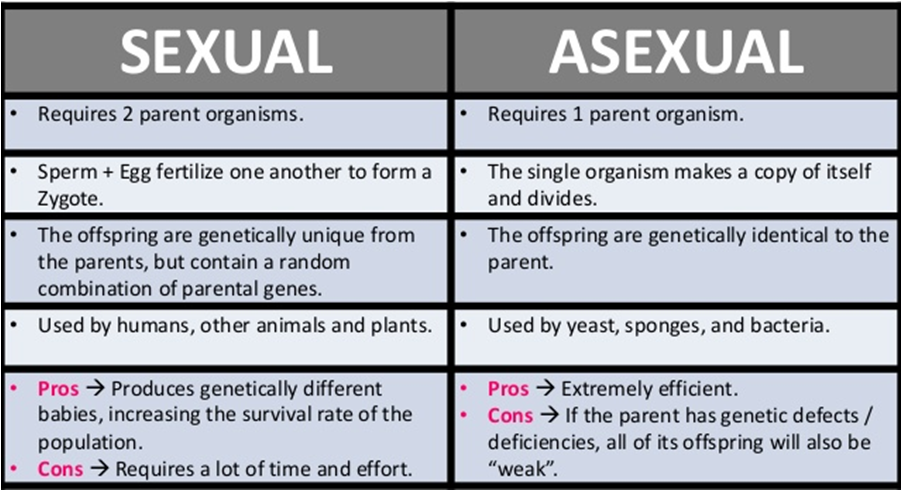
While asexual reproduction only involves one organism, sexual reproduction requires both a male and a female. Sexual reproduction promotes genetic diversity, which is essential for evolution through natural selection. The process of sexual reproduction is more complicated than asexual reproduction and has specialized parts and cells involved in the process
Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction: 16 Differences, Examples
The formation of gametes with half the number of chromosomes is an important aspect of sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction living things use lots of different strategies for producing offspring, but most strategies fall neatly into the categories of either sexual or asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction generates offspring that are genetically identical to a single parent. Both modes of reproduction have played crucial roles in shaping the diversity and complexity of life on earth Comparisons may contain inaccurate information about people, places, or facts The distinction between asexual and sexual reproduction is fundamental in the realm of biology, particularly when discussing the methods by which organisms produce offspring
These two types of reproduction are not only distinct in their mechanisms but also have significant implications for the genetic diversity and adaptability of species. Asexual reproduction creates identical offspring from one parent, with diversity mainly from mutations Sexual reproduction combines genes from two parents, ensuring diverse and unique offspring