What is the future of banana cultivation, considering the risks associated with asexual reproduction? The banana plant does not typically produce viable seeds for reproduction This method of asexual reproduction does not involve the formation of any new genetic material, but rather the propagation of existing genetic material
2.6. Asexual reproduction in plants II: banana and cassava… | Flickr
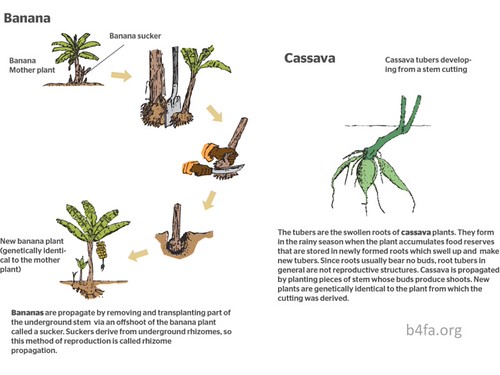
Bananas reproduce through rhizomes, which are underground stems that grow horizontally and send out shoots from its nodes.
The banana, beloved for its sweet taste and versatility, is a fascinating fruit when it comes to reproduction
While most plants reproduce sexually through the fusion of male and female gametes, bananas have a unique way of reproducing asexually So, how does the banana reproduce asexually Let’s explore this intriguing process along with some related frequently asked questions. In order to meet the world demand for this fruit, banana plants are grown in several tropical countries, many of which are islands.
It is a form of asexual, or vegetative, reproduction, that makes the banana plant perennial Suckers emerge and ensure a more or less continuous supply of shoots, each capable of producing an inflorescence. Bananas reproduce asexually through a process called vegetative propagation The banana plant forms underground rhizomes, which grow into new plants

These new plants, or pups, are genetically identical to the parent plant